What is a Business Model and How to Know if It Works?
M Consulting Business Co., Ltd.
Issue 5 | January 1, 2025
Welcome to Issue 5 of M Consulting Business Insight: "What is a Business Model and How to Know if It Works?"
In this issue, we explore how businesses can refine their strategies, adopt innovative frameworks, and stand out in 2025's competitive market.
Introduction
As we begin 2025, having a clear and adaptable business model is more important than ever. A business model forms the backbone of any company, guiding how value is delivered to customers and profitability is achieved. For businesses in Thailand, staying competitive in a rapidly changing market requires continuous refinement of their strategies.
📥 Prefer offline reading?
You can download the full article in PDF format here:
Download Issue 5 (PDF)
Why Your Business Model Matters
A business model is not just a plan; it's a blueprint for success. It defines how your company operates, serves customers, and generates revenue. Whether you're a startup or an established business, refining your business model ensures long-term sustainability and growth.
Key Components of a Business Model
To understand how a business model works, focus on these critical elements:
Value Proposition: What unique problem does your business solve?
Target Market: Who are your ideal customers?
Revenue Streams: How does your business generate income?
Cost Structure: What are the main costs involved?
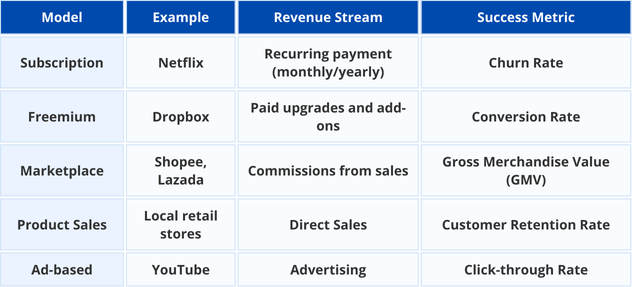
Types of Business Models and Their Metrics
Different industries benefit from varying business models. Here are some popular examples:
1. Subscription Model
Revenue is generated through recurring fees, as seen with Netflix.
Key Metric: Churn Rate – the percentage of customers who cancel their subscription.
2. Freemium Model
Free basic services are offered, with premium features available for purchase, like Dropbox.
Key Metric: Conversion Rate – the percentage of free users who upgrade.
3. Marketplace Model
Platforms like Shopee connect buyers and sellers, earning commissions on sales.
Key Metric: Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) – the total sales transacted through the platform.
4. Product Sales Model
Traditional retail businesses, such as local shops, rely on direct sales.
Key Metric: Customer Retention Rate – the percentage of repeat customers.
5. Ad-Based Model
Revenue is generated through advertisements, as seen with YouTube.
Key Metric: Click-Through Rate (CTR) – the percentage of users who click on ads.
Table 1: Comparison of different business models, examples, and key success metrics.
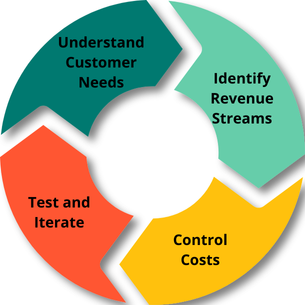
How to Develop and Test Your Business Model
Testing and refining your business model ensures it stays relevant and effective. Follow these steps:
1. Understand Customer Needs
Analyze your target audience to identify pain points and preferences. Use surveys or analytics tools for insights.
2. Identify Revenue Streams
Diversify income sources by exploring new opportunities, such as online channels or partnerships.
3. Control Costs
Optimize your cost structure by using efficient suppliers or automating repetitive tasks.
4. Test and Iterate
Experiment with tools like the Business Model Canvas (BMC) or SWOT Analysis to identify strengths and weaknesses.
Figure 1: Key steps include understanding customer needs, identifying revenue streams, controlling costs, and iterating for improvement.
The flowchart outlines
Understand Customer Needs
Identify Revenue Streams
Control Costs
Test and Iterate
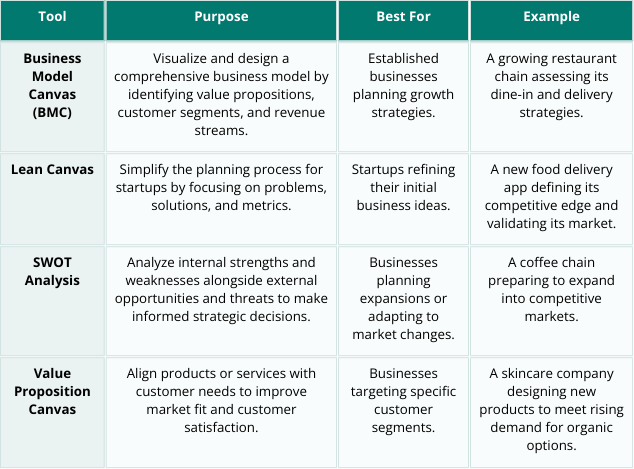
Tools for Building Better Business Models
Use these tools to design or refine your business strategy:
Business Model Canvas (BMC): Visualize key elements like customer segments and revenue streams.
Lean Canvas: Focus on problem-solving for startups.
SWOT Analysis: Analyze strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Value Proposition Canvas: Align your offerings with customer needs for a stronger market fit.
Table 2: A guide to tools for creating and refining business models, with examples and best use cases.
Lessons from Successes and Failures
Success Stories
Zen Corporation Group (Thailand): Expanded its restaurant portfolio by acquiring Tummour while preserving its brand identity.
Amazon: Scaled globally through innovation and customer-centric services like Prime memberships.
Failure Examples
Thai Airways: Struggled due to high costs and failure to compete with low-cost carriers.
Kodak: Lost market dominance by clinging to traditional film despite the rise of digital photography.
Measuring Success in Your Business Model
Key Success Indicators
Revenue Growth: Indicates strong product-market fit.
Customer Retention: Reflects satisfaction and loyalty.
Profitability: Ensures long-term viability.
Scalability: Shows potential for growth without proportional cost increases.
Warning Signs
Flat sales or high churn rates.
Rising operational costs.
Resistance to adopting new technology or market trends.
Conclusion: Build a Resilient Business Model in 2025
Success in today’s competitive market requires adaptability, customer focus, and operational excellence. By leveraging tools like the Business Model Canvas, learning from case studies, and continuously testing strategies, your business can thrive.
📩 Contact Us Today: info@m-consultingbiz.com
🌐 Visit Our Website: www.m-consultingbiz.com
Let’s build a stronger future together!